ScatterPlotWithTwoHists¶
- class lsst.analysis.tools.actions.plot.ScatterPlotWithTwoHists(*args, **kw)¶
Bases:
PlotActionMakes a scatter plot of the data with a marginal histogram for each axis.
Attributes Summary
Add a summary plot to the figure? (
bool, defaultTrue)Apply a
Contextto anAnalysisActionrecursively.If a configurable action is assigned to a
ConfigurableActionField, or aConfigurableActionStructFieldthe name of the field will be bound to this variable when it is retrieved.Legend position within main plot (
str, default'upper left')Label to use for the magnitudes used for SNR (
str)Number of bins on x axis (
float, default40.0)Plot a 2D histogram in dense areas of points on the scatter plot.Doesn't look great if plotting multiple datasets on top of each other.
Selection of types of objects to plot.
Label to use for the x axis (
str)xlimits of the plot, if not specified determined from data (
List, defaultNone)Label to use for the y axis (
str)ylimits of the plot, if not specified determined from data (
List, defaultNone)Methods Summary
__call__(data, **kwargs)Call self as a function.
addInputSchema(inputSchema)Add the supplied inputSchema argument to the class such that it will be returned along side any other arguments in a call to
getInputSchema.compare(other[, shortcut, rtol, atol, output])Compare this configuration to another
Configfor equality.formatHistory(name, **kwargs)Format a configuration field's history to a human-readable format.
freeze()Make this config, and all subconfigs, read-only.
getFormattedInputSchema(**kwargs)Return input schema, with keys formatted with any arguments supplied by kwargs passed to this method.
Return the schema an
AnalysisActionexpects to be present in the arguments supplied to the __call__ method.getOutputNames([config])Returns a list of names that will be used as keys if this action's call method returns a mapping.
Return the schema an
AnalysisActionwill produce, if the__call__method returnsKeyedData, otherwise this may return None.items()Get configurations as
(field name, field value)pairs.keys()Get field names.
load(filename[, root])Modify this config in place by executing the Python code in a configuration file.
loadFromStream(stream[, root, filename, ...])Modify this Config in place by executing the Python code in the provided stream.
loadFromString(code[, root, filename, ...])Modify this Config in place by executing the Python code in the provided string.
makePlot(data, skymap, plotInfo, **kwargs)Makes a generic plot with a 2D histogram and collapsed histograms of each axis.
names()Get all the field names in the config, recursively.
save(filename[, root])Save a Python script to the named file, which, when loaded, reproduces this config.
saveToStream(outfile[, root, skipImports])Save a configuration file to a stream, which, when loaded, reproduces this config.
saveToString([skipImports])Return the Python script form of this configuration as an executable string.
Subclass hook for computing defaults.
toDict()Make a dictionary of field names and their values.
update(**kw)Update values of fields specified by the keyword arguments.
validate()Validate the Config, raising an exception if invalid.
values()Get field values.
Attributes Documentation
- applyContext¶
Apply a
Contextto anAnalysisActionrecursively.Generally this method is called from within an
AnalysisToolto configure allAnalysisActions at one time to make sure that they all are consistently configured. However, it is permitted to call this method if you are aware of the effects, or from within a specific execution environment like a python shell or notebook.- Parameters:
- context
Context The specific execution context, this may be a single context or a joint context, see
Contextfor more info.
- context
- history¶
Read-only history.
- identity: str | None = None¶
If a configurable action is assigned to a
ConfigurableActionField, or aConfigurableActionStructFieldthe name of the field will be bound to this variable when it is retrieved.
- plot2DHist¶
Plot a 2D histogram in dense areas of points on the scatter plot.Doesn’t look great if plotting multiple datasets on top of each other. (
bool, defaultTrue)
- plotTypes¶
Selection of types of objects to plot. Can take any combination of stars, galaxies, unknown, any (
List)
- xLims¶
xlimits of the plot, if not specified determined from data (
List, defaultNone)
- yLims¶
ylimits of the plot, if not specified determined from data (
List, defaultNone)
Methods Documentation
- __call__(data: MutableMapping[str, ndarray[Any, dtype[ScalarType]] | Scalar | HealSparseMap | Tensor], **kwargs) Mapping[str, Figure] | Figure¶
Call self as a function.
- addInputSchema(inputSchema: Tensor]]]) None¶
Add the supplied inputSchema argument to the class such that it will be returned along side any other arguments in a call to
getInputSchema.- Parameters:
- inputSchema
KeyedDataSchema A schema that is to be merged in with any existing schema when a call to
getInputSchemais made.
- inputSchema
- compare(other, shortcut=True, rtol=1e-08, atol=1e-08, output=None)¶
Compare this configuration to another
Configfor equality.- Parameters:
- other
lsst.pex.config.Config Other
Configobject to compare against this config.- shortcut
bool, optional If
True, return as soon as an inequality is found. Default isTrue.- rtol
float, optional Relative tolerance for floating point comparisons.
- atol
float, optional Absolute tolerance for floating point comparisons.
- outputcallable, optional
A callable that takes a string, used (possibly repeatedly) to report inequalities.
- other
- Returns:
- isEqual
bool Truewhen the twolsst.pex.config.Configinstances are equal.Falseif there is an inequality.
- isEqual
See also
Notes
Unselected targets of
RegistryFieldfields and unselected choices ofConfigChoiceFieldfields are not considered by this method.Floating point comparisons are performed by
numpy.allclose.
- formatHistory(name, **kwargs)¶
Format a configuration field’s history to a human-readable format.
- Parameters:
- name
str Name of a
Fieldin this config.- **kwargs
Keyword arguments passed to
lsst.pex.config.history.format.
- name
- Returns:
- history
str A string containing the formatted history.
- history
See also
- freeze()¶
Make this config, and all subconfigs, read-only.
- getFormattedInputSchema(**kwargs) Tensor]]]¶
Return input schema, with keys formatted with any arguments supplied by kwargs passed to this method.
- Returns:
- result
KeyedDataSchema The schema this action requires to be present when calling this action, formatted with any input arguments (e.g. band=’i’)
- result
- getInputSchema() Tensor]]]¶
Return the schema an
AnalysisActionexpects to be present in the arguments supplied to the __call__ method.- Returns:
- result
KeyedDataSchema The schema this action requires to be present when calling this action, keys are unformatted.
- result
- getOutputNames(config: Config | None = None) Iterable[str]¶
Returns a list of names that will be used as keys if this action’s call method returns a mapping. Otherwise return an empty Iterable.
- Parameters:
- config
lsst.pex.config.Config, optional Configuration of the task. This is only used if the output naming needs to be config-aware.
- config
- Returns:
- result
Iterableofstr If a
PlotActionproduces more than one plot, this should be the keys the action will use in the returnedMapping.
- result
- getOutputSchema() Tensor]]] | None¶
Return the schema an
AnalysisActionwill produce, if the__call__method returnsKeyedData, otherwise this may return None.- Returns:
- result
KeyedDataSchemaor None The schema this action will produce when returning from call. This will be unformatted if any templates are present. Should return None if action does not return
KeyedData.
- result
- items()¶
Get configurations as
(field name, field value)pairs.- Returns:
- items
ItemsView Iterator of tuples for each configuration. Tuple items are:
Field name.
Field value.
- items
- keys()¶
Get field names.
- Returns:
- names
KeysView List of
lsst.pex.config.Fieldnames.
- names
- load(filename, root='config')¶
Modify this config in place by executing the Python code in a configuration file.
- Parameters:
- filename
str Name of the configuration file. A configuration file is Python module.
- root
str, optional Name of the variable in file that refers to the config being overridden.
For example, the value of root is
"config"and the file contains:config.myField = 5
Then this config’s field
myFieldis set to5.
- filename
- loadFromStream(stream, root='config', filename=None, extraLocals=None)¶
Modify this Config in place by executing the Python code in the provided stream.
- Parameters:
- streamfile-like object,
str,bytes, orCodeType Stream containing configuration override code. If this is a code object, it should be compiled with
mode="exec".- root
str, optional Name of the variable in file that refers to the config being overridden.
For example, the value of root is
"config"and the file contains:config.myField = 5
Then this config’s field
myFieldis set to5.- filename
str, optional Name of the configuration file, or
Noneif unknown or contained in the stream. Used for error reporting.- extraLocals
dictofstrtoobject, optional Any extra variables to include in local scope when loading.
- streamfile-like object,
See also
Notes
For backwards compatibility reasons, this method accepts strings, bytes and code objects as well as file-like objects. New code should use
loadFromStringinstead for most of these types.
- loadFromString(code, root='config', filename=None, extraLocals=None)¶
Modify this Config in place by executing the Python code in the provided string.
- Parameters:
- code
str,bytes, orCodeType Stream containing configuration override code.
- root
str, optional Name of the variable in file that refers to the config being overridden.
For example, the value of root is
"config"and the file contains:config.myField = 5
Then this config’s field
myFieldis set to5.- filename
str, optional Name of the configuration file, or
Noneif unknown or contained in the stream. Used for error reporting.- extraLocals
dictofstrtoobject, optional Any extra variables to include in local scope when loading.
- code
- Raises:
- ValueError
Raised if a key in extraLocals is the same value as the value of the root argument.
- makePlot(data: MutableMapping[str, ndarray[Any, dtype[ScalarType]] | Scalar | HealSparseMap | Tensor], skymap: BaseSkyMap, plotInfo: Mapping[str, str], **kwargs) Figure¶
Makes a generic plot with a 2D histogram and collapsed histograms of each axis.
- Parameters:
- data
KeyedData The catalog to plot the points from.
- skymap
lsst.skymap.BaseSkyMap The skymap that gives the patch locations
- plotInfo
dict A dictionary of information about the data being plotted with keys:
- data
- Returns:
- fig
matplotlib.figure.Figure The resulting figure.
- fig
Notes
Uses the axisLabels config options
xandyand the axisAction config optionsxActionandyActionto plot a scatter plot of the values against each other. A histogram of the points collapsed onto each axis is also plotted. A summary panel showing the median of the y value in each patch is shown in the upper right corner of the resultant plot. The code uses the selectorActions to decide which points to plot and the statisticSelector actions to determine which points to use for the printed statistics.If this function is being used within the pipetask framework that takes care of making sure that data has all the required elements but if you are running this as a standalone function then you will need to provide the following things in the input data.
- If stars is in self.plotTypes:
xStars, yStars, starsHighSNMask, starsLowSNMask and {band}_highSNStars_{name}, {band}_lowSNStars_{name} where name is median, sigma_Mad, count and approxMag.
If it is for galaxies/unknowns then replace stars in the above names with galaxies/unknowns.
If it is for any (which covers all the points) then it becomes, x, y, and any instead of stars for the other parameters given above.
- In every case it is expected that data contains:
lowSnThreshold, highSnThreshold and patch (if the summary plot is being plotted).
Examples
An example of the plot produced from this code is here:
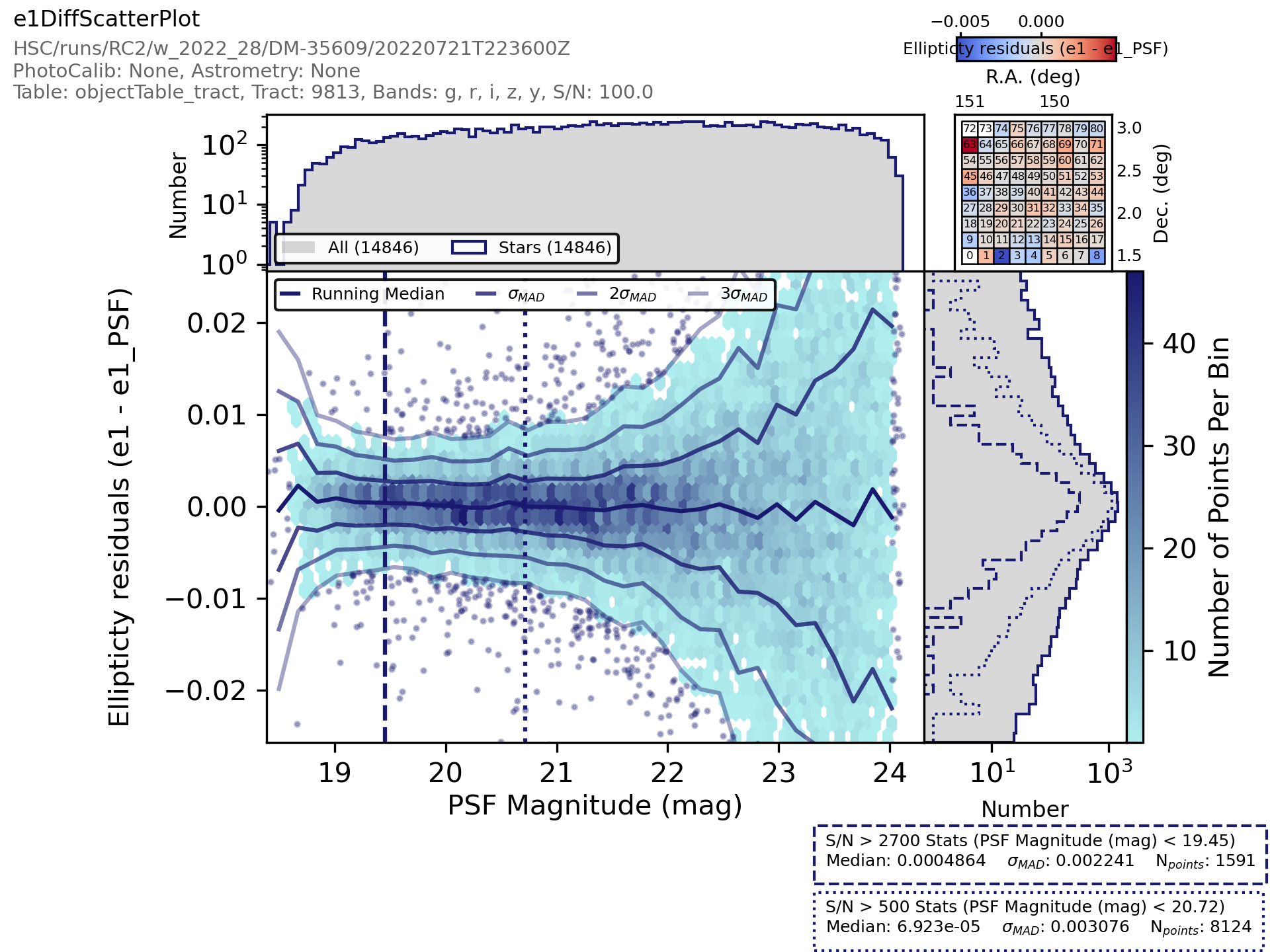
For a detailed example of how to make a plot from the command line please see the getting started guide.
- save(filename, root='config')¶
Save a Python script to the named file, which, when loaded, reproduces this config.
- Parameters:
- filename
str Desination filename of this configuration.
- root
str, optional Name to use for the root config variable. The same value must be used when loading (see
lsst.pex.config.Config.load).
- filename
- saveToStream(outfile, root='config', skipImports=False)¶
Save a configuration file to a stream, which, when loaded, reproduces this config.
- Parameters:
- outfilefile-like object
Destination file object write the config into. Accepts strings not bytes.
- root
str, optional Name to use for the root config variable. The same value must be used when loading (see
lsst.pex.config.Config.load).- skipImports
bool, optional If
Truethen do not includeimportstatements in output, this is to support human-oriented output frompipetaskwhere additional clutter is not useful.
- saveToString(skipImports=False)¶
Return the Python script form of this configuration as an executable string.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
- code
str A code string readable by
loadFromString.
- code
- setDefaults()¶
Subclass hook for computing defaults.
Notes
Derived
Configclasses that must compute defaults rather than using theFieldinstances’s defaults should do so here. To correctly use inherited defaults, implementations ofsetDefaultsmust call their base class’ssetDefaults.
- toDict()¶
Make a dictionary of field names and their values.
See also
Notes
This method uses the
toDictmethod of individual fields. Subclasses ofFieldmay need to implement atoDictmethod for this method to work.
- update(**kw)¶
Update values of fields specified by the keyword arguments.
- Parameters:
- **kw
Keywords are configuration field names. Values are configuration field values.
Notes
The
__atand__labelkeyword arguments are special internal keywords. They are used to strip out any internal steps from the history tracebacks of the config. Do not modify these keywords to subvert aConfiginstance’s history.Examples
This is a config with three fields:
>>> from lsst.pex.config import Config, Field >>> class DemoConfig(Config): ... fieldA = Field(doc='Field A', dtype=int, default=42) ... fieldB = Field(doc='Field B', dtype=bool, default=True) ... fieldC = Field(doc='Field C', dtype=str, default='Hello world') ... >>> config = DemoConfig()
These are the default values of each field:
>>> for name, value in config.iteritems(): ... print(f"{name}: {value}") ... fieldA: 42 fieldB: True fieldC: 'Hello world'
Using this method to update
fieldAandfieldC:>>> config.update(fieldA=13, fieldC='Updated!')
Now the values of each field are:
>>> for name, value in config.iteritems(): ... print(f"{name}: {value}") ... fieldA: 13 fieldB: True fieldC: 'Updated!'
- validate()¶
Validate the Config, raising an exception if invalid.
- Raises:
- lsst.pex.config.FieldValidationError
Raised if verification fails.
Notes
The base class implementation performs type checks on all fields by calling their
validatemethods.Complex single-field validation can be defined by deriving new Field types. For convenience, some derived
lsst.pex.config.Field-types (ConfigFieldandConfigChoiceField) are defined inlsst.pex.configthat handle recursing into subconfigs.Inter-field relationships should only be checked in derived
Configclasses after calling this method, and base validation is complete.
- values()¶
Get field values.
- Returns:
- values
ValuesView Iterator of field values.
- values